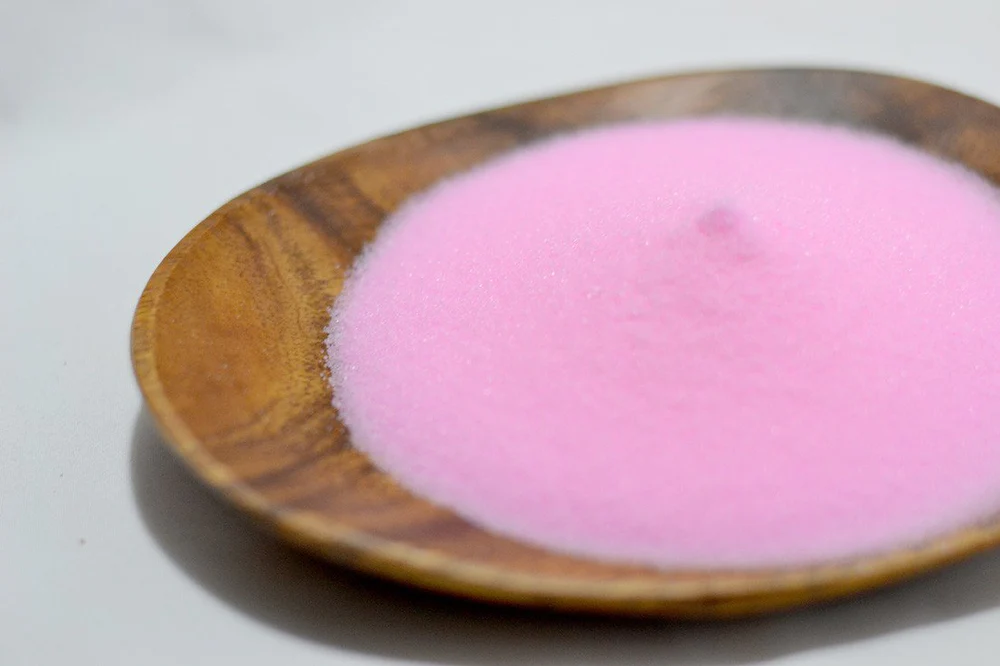
Pink curing salt, commonly referred to as Prague Powder or curing salt #1, is a specialized salt blend used primarily in the meat curing process. Unlike regular table salt, which is primarily composed of sodium chloride, pink curing salt contains sodium nitrite, as well as a small percentage of sodium chloride. The presence of sodium nitrite acts as a crucial preservative, inhibiting the growth of harmful bacteria, most notably Clostridium botulinum, which can cause botulism—a serious foodborne illness.
The distinctive pink color of this curing salt serves a dual purpose. Firstly, it helps to differentiate it from regular salt to prevent accidental consumption due to its toxic ingredient (sodium nitrite) in large quantities. Secondly, the pigment enhances the visual appeal of cured meats, imparting an appealing hue that many consumers associate with fresh, cured products.
In the curing process, pink curing salt plays an integral role, not only in preservation but also in flavor enhancement. The nitrites react with myoglobin in the meat, leading to the formation of stable pink pigments that lend cured meats their characteristic color. This reaction also contributes to the unique flavor profiles associated with various cured products, such as bacon, ham, and salami. Moreover, the preservation properties provided by the nitrites can extend the shelf life of meat products while ensuring they remain safe for consumption.
While pink curing salt is essential for the curing of meats, it is important to use it in the recommended quantities since excessive consumption can lead to health risks. Understanding the unique properties of pink curing salt and its vital role in food safety and flavor enhancement serves as a foundational element for anyone interested in curing meats at home or professionally.
The Role of Pink Curing Salt in Food Preservation
Pink curing salt, also known as Prague Powder or curing salt #1, plays a crucial role in the preservation of meats. This specialized salt comprises sodium chloride and sodium nitrite, the latter being responsible for inhibiting bacterial growth, specifically that of the pathogenic bacteria Clostridium botulinum, which can lead to botulism. The nitrite component effectively protects against spoilage by preventing microorganisms from thriving in cured meats.
In addition to its preservative qualities, pink curing salt is instrumental in developing the distinctive color and flavor associated with cured meats. When applied, it reacts with the meat’s myoglobin, a protein in muscle tissue, resulting in the characteristic rosy hue that consumers often expect from cured products such as bacon and salami. This color change not only appeals to the eye but also indicates the meat has undergone proper curing processes, enhancing its overall marketability.
The enhancement of flavor is another key benefit of using pink curing salt. The nitrite content contributes to the savory, umami flavor profile found in many cured meats. This unique flavor, coupled with the product’s tangy freshness, creates an enjoyable eating experience. Furthermore, the curing process affects the texture of the meat; it becomes firmer and more succulent, accentuating its palatability.
It is imperative, however, that the correct amounts of pink curing salt are utilized, as excessive ingestion of nitrites may pose health risks. Following established guidelines and recipes ensures both safety and quality in the curing process. Proper use of pink curing salt not only preserves the meat effectively but also enhances its sensory attributes, making it a vital ingredient in traditional curing practices.
Health and Safety Concerns of Using Pink Curing Salt
Pink curing salt, also known as Prague Powder No. 1 or curing salt #1, is commonly used in the preservation of meats. However, its primary active ingredient, sodium nitrite, raises several health and safety concerns. It is essential to understand the appropriate levels of nitrite consumption and the potential risks associated with overconsumption when using this product.
Nitrites, when consumed in moderation, can contribute to the prevention of botulism and maintain the characteristic pink color of cured meats. The acceptable daily intake (ADI) for sodium nitrite is generally considered to be 0.06 mg per kilogram of body weight. However, exceeding these amounts can lead to nitrite poisoning, presenting symptoms such as headache, dizziness, and gastrointestinal distress.
Moreover, nitrites can undergo a chemical reaction in the body to form nitrosamines, which are potentially carcinogenic compounds. This risk tends to increase when cured meats are charred or cooked at high temperatures. Therefore, maintaining moderation and balancing the consumption of cured products is crucial in minimizing the health risks associated with pink curing salt.
Besides dietary considerations, safety precautions are critical when handling pink curing salt. It is advisable to wear gloves and a mask when mixing or handling curing salts to avoid inhalation or skin contact. Proper storage is also vital; the curing salt should be kept in a cool, dry place, away from sunlight and moisture. Additionally, it must be stored out of reach of children to prevent accidental ingestion.
All in all, while pink curing salt is a valuable ingredient for meat preservation, it is important to be conscientious about usage. Adhering to suggested guidelines and understanding the implications of sodium nitrite can ensure a safe and enjoyable experience in culinary practices.
Alternatives to Pink Curing Salt:
Pink curing salt, renowned for its unique properties in the curing process, may not always be readily available or suitable for all culinary applications. Fortunately, several alternatives can be effectively utilized for curing meat, each with its advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these substitutes can help maintain flavor and preservation effects similar to those achieved with pink curing salt.
One of the most common alternatives is plain salt, which can be used for basic curing purposes. While it does not provide the distinctive flavor and color imparted by pink curing salt, it can still effectively enhance the taste and preservation of meats. It is important to note that when using plain salt, one may miss out on the specific preservation benefits of sodium nitrite found in pink curing salt.
Another alternative is a combination of kosher salt and a small amount of sugar or honey. This mixture can mirror the sweet and savory balance typically created through the use of pink curing salt. Additionally, it can contribute to a more rounded flavor profile. However, the absence of nitrite in this concoction may lead to a shorter shelf life for cured meats.
Spices such as garlic powder, black pepper, and juniper berries can also serve as flavor enhancers when curing meats without pink curing salt. Each spice contributes a unique taste, although they do not fulfill the preservation role of nitrates. Therefore, while they enhance flavor, they should ideally be used in combination with salts that include curing agents.
In conclusion, while pink curing salt offers specific benefits for meat curing, various alternatives and natural spices exist. By considering the pros and cons of these substitutes, one can achieve satisfactory results in flavor and preservation, even when pink curing salt is not an option.
How to Properly Use Pink Curing Salt in Meat Curing?
When it comes to meat curing, the incorporation of pink curing salt, also known as Prague Powder or curing salt, is vital for both flavor enhancement and food safety. Understanding the correct usage is crucial for successful curing outcomes. First, it is important to note that the primary safety agent in pink curing salt is sodium nitrite, which helps prevent botulism and contributes to the meat’s characteristic flavor and color. The following steps outline how to effectively use pink curing salt in the meat curing process.
Begin by selecting the appropriate type of meat for curing, such as pork, beef, or poultry. The measurement of pink curing salt is generally prescribed at a ratio of 1 ounce per 25 pounds of meat. This equates to approximately 0.25% of the total weight of the meat, ensuring that the nitrite levels remain safe and effective. For smaller batches, a precision scale can help measure smaller quantities accurately.
Next, mix the pink curing salt with any desired spices or sugar to create a curing mixture. It is advisable to dissolve the salt in a small amount of water to help distribute it evenly when applying. Rub this mixture thoroughly over the surface of the meat, ensuring complete coverage. It is essential to work the mixture into the meat, particularly in the case of larger cuts, to ensure that the curing salt penetrates adequately.
Following the application, place the meat in a vacuum-sealed bag or a non-reactive container and refrigerate it. Curing times may vary from several days to weeks, depending on the type of meat and the thickness of the cut. Monitoring the temperature consistently during the curing process is critical. Finally, always keep in mind the recommended guidelines for safe meat preservation to ensure optimal results while using pink curing salt.
Where to Buy Pink Curing Salt?
When it comes to sourcing pink curing salt, consumers have a variety of avenues to explore. This specialized curing agent, also known as Prague Powder or curing salt #1, is essential for preserving and flavoring meats while ensuring safety by preventing botulism. The growing interest in home curing has made it increasingly accessible, and you can find it through several purchasing options.
One of the most convenient ways to buy pink curing salt is through online retailers. Websites such as Amazon, Walmart, and specialty culinary sites often stock this product, offering various brands and package sizes. The benefit of online shopping is that it allows you to compare prices, read customer reviews, and sometimes obtain bulk purchasing discounts. When shopping online, it is advisable to verify the seller’s credibility and ensure that the product specifies its purpose and contains the necessary ingredients.
Local butchers and meat markets are also excellent venues to consider for acquiring pink curing salt. Many butchers not only sell high-quality meats but also carry essential curing supplies. By purchasing from local sources, you can directly inquire about the salt’s quality, usage, and even request recommendations for curing techniques. Furthermore, supporting local businesses contributes positively to the community.
Specialty food stores provide another option. Stores that focus on gourmet ingredients often have sections dedicated to curing agents and spices. These establishments may also offer unique variations of pink curing salt, suitable for different applications, such as bacon, sausages, or charcuterie boards. Make sure to check if the product adheres to industry standards, ensuring you’re choosing a safe and effective option.
In summary, whether opting for online retailers, local butchers, or specialty food stores, finding quality pink curing salt has never been easier. Each source offers distinct advantages, so choose one that aligns with your preferences and needs.
Popular Recipes Using Pink Curing Salt
Pink curing salt, also known as Prague Powder #1, is an essential ingredient for various cured meat recipes, adding both flavor and preserving properties. Traditional methods of meat curing have been refined over the years, allowing home cooks and professional chefs alike to explore their creativity with this unique substance. Below are several recipes that incorporate pink curing salt, showcasing its versatility.
One of the most popular cured meat preparations is bacon. To prepare homemade bacon, one starts with a pork belly weighing approximately 5 to 10 pounds. A brine is made using a mixture of kosher salt, pink curing salt, brown sugar, and your choice of spices like pepper or garlic powder. This mixture is rubbed over the pork belly and stored in the refrigerator for about a week, turning occasionally. After curing, the belly is rinsed, dried, and then smoked or baked until it reaches a desirable doneness.
Another classic is homemade ham. Similar to bacon, the process requires a brine solution that includes pink curing salt. A whole ham should be submerged in the brine for about 10 days, allowing the flavors to penetrate deeply and ensuring safe preservation. After the curing period, the ham can be baked or smoked to enhance its flavor profile.
Salami is another staple among cured meats, particularly beneficial for those looking to experiment with various flavors. To create salami, ground pork or beef is mixed with spices, wine, and pink curing salt. This mixture is then stuffed into casings and hung to ferment in a controlled environment. The drying process can take several weeks, resulting in a flavorful and preservative-rich product.
These recipes highlight how pink curing salt plays a crucial role in both traditional and contemporary meat curing techniques. By utilizing pink curing salt, cooks can achieve both safety and flavor in their cured meat endeavors.
The History and Culture of Curing Meats:
Curing meats is a practice that dates back thousands of years, originating as a method of food preservation before the advent of refrigeration. In ancient cultures, salt was recognized for its ability to inhibit bacterial growth, thus extending the shelf life of meats and ensuring a stable supply of food. The understanding and use of different curing agents have developed over time, reflecting local customs, resources, and culinary preferences.
In the early days, various methods of curing were adopted by different societies, with salt being the most prevalent. Regions like the Mediterranean relied on sea salt, while those in Northern Europe utilized rock salt for their curing processes. The introduction of pink curing salt, which contains sodium nitrite, revolutionized the practice, as it not only preserved meat effectively but also endowed it with a distinct color and flavor. The incorporation of nitrites into curing processes not only enhances safety but also contributes to the recognized pink hue of cured meats, appealing to consumers’ visual appetites.
Cultural significance surrounding cured meats varies widely across the globe, with certain specialties becoming emblematic of national or regional identities. For example, Italian prosciutto, Spanish jamón, and French saucisson illustrate how meat curing reflects local traditions and the availability of resources. Many of these traditions have been passed down through generations, whereby families preserve their unique recipes and techniques. In some cultures, the process of curing is even associated with festivity and community gathering, often celebrated with large family or community meals featuring these flavorful products.
As the demand for artisanal and traditional methods has surged in contemporary culinary practice, the use of pink curing salt and similar substitutes has gained prominence. These advancements serve not only to preserve meat but to keep alive the cultural narrative that embraces the art of meat curing. The interplay between history, culture, and technology underscores the enduring significance of meat curing in our contemporary culinary landscape.
Conclusion: Embracing Pink Curing Salt in Your Culinary Adventures
In summary, pink curing salt is a vital ingredient for both professional chefs and home cooks seeking to expand their culinary repertoire. This unique curing agent not only plays a critical role in preserving meats but also contributes to the development of flavors during the curing process. Understanding the nature of pink curing salt, including its ingredients and how it differs from regular table salt, is vital for anyone interested in mastering the art of meat curing. By adhering to safe practices when using this curing salt, cooks can enjoy the benefits of added flavor and preservation without compromising their health.
Throughout this guide, we have explored the various uses of pink curing salt, ranging from traditional meat products like sausages and hams to innovative culinary experiments with fish and vegetables. Using pink curing salt can elevate ordinary dishes to gourmet experiences when applied correctly. Cooks are encouraged to embrace not only the practical aspects of curing meats but also the creativity involved in experimenting with different flavor profiles and curing methods.
Moreover, while pink curing salt provides numerous benefits, it is important to consider suitable substitutes when necessary and to remain informed about the safety measures required in curing processes. The incorporation of this specialized salt into your cooking journey opens up a world of possibilities, enabling you to craft deli-quality items in the comfort of your kitchen. Thus, we invite you to dive into the world of meat curing and explore the advantages and joys of using pink curing salt, enhancing your meals and impressing your guests along the way.